(1)定义:在位于给定点并具有相同自旋的参考电子的邻域中找到电子的可能性的量度
(2)作用:用于表征电子的局域化分布特征,ELF的值在0-1之间,取上限1表示电子完全局域化,取0值表示电子完全离域化,取1/2则表示该处电子形成了类似于电子气的电子对分布。
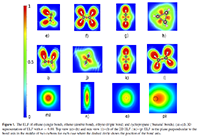
(3)说明:From the 2D ELF in figures 1(g) and (k) it is easily seen that the three bond domains are degenerate and merged into a torus which means that σ and π bonds separation is not observed, similar to the case of ethene double bond where it is also not possible to observe individually the π and the σ bond. This is clearly shown in figure 1(o), which is the 2D ELF representation of the plane perpendicular to the bond axis, where ELF is zero at the center of the torus. The population of the torus (ELF basin) is 5.3 electrons. We also analyze the special case of 'banana bonds' in cyclopropane (C3H3) with ELF. The localized electrons are not centered on the bond axis but they are found mostly on the outside of the bond axis (figures 1(d) and (h)). This can be seen clearly in figure 1(p) where the dashed circle represents the bond axis. The population of this ELF basin is 1.8 electrons, which is the same as for ethane. The shape of the ELF is however different from the single bond in ethane, as can be seen in the top view (figure 1(h)) that looks almost triangular compare to the rectangular shape in figure 1(e). The ELF description of the cyclopropane bonds is consistent with previous studies [33]. A common ELF characteristic of all these covalent bonds are the non-nuclear maxima which are present in the interaction region. However, the properties of covalent bonds are rather well studied and well understood [34], and the ELF analysis is in agreement with common knowledge.
文献来源:https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-648X/ab7fd8
第一性原理计算的基本思想是将多个原子构成的体系看成是由多个电子和原子核组成的系统,并根据量子力学的基本原理对问题进行最大限度的“非经验性”处理。它只需要5个基本常数(m0,e,h,c,kB)就可以计算出体系的能量和电子结构等物理性质。它可以确定已知材料的结构和基础性质,并实现原子级别的精准控制,是现阶段解决实验理论问题和预测新材料结构性能的有力工具。并且,第一性原理计算不需要开展真实的实验,极大地节省了实验成本,现已被广泛应用于化学、物理、生命科学和材料学等领域。
适合的研究方向包括但不限于:催化、电池、半导体、金属材料、非金属材料、合金、纳米材料等
可以计算的体系包括但不限于:晶体、非晶、二维材料、表面、界面、固体等
常用软件:VASP,MS,CP2K,QE等
可以计算的内容包括但不限于:
材料的几何结构参数(如键长、键角、二面角、晶格常数、原子位置等)
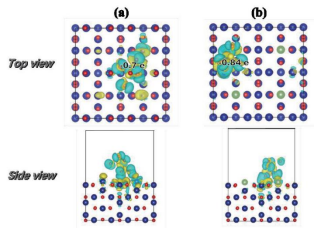
材料的电子结构信息(如电荷密度、电荷差分密度、态密度、能带、费米能级、功函数、ELF等)
材料的光学性质(如介电常数等)
材料的力学性质(如弹性模量等)
材料的磁学性质(如磁导率等)
材料的晶格动力学性质(如声子谱等)
材料的表面性质(如吸附能,催化计算等)
复合材料的性质(异质结等内容)等等