(1)定义及意义
体系中电子总是分布在无穷大的三维空间中。为了方便地研究体系的电性特征,可以设法将三维空间分割为一系列原子空间,每个子空间内的电子认为“从属于”某个原子,由此可以得到被归属于每个原子的电子数,与核电荷数相减得到原子电荷。由此可以辅助判断哪些原子相对带正电或负电。
原子电荷是基于对实空间的分割而得到的不可测量,根据空间分割方式而存在多种定义,如Mulliken电荷、Bader(AIM)电荷、Hirshfeld电荷等,不同电荷定义方式各有特点,适用于不同场合,定性定量互有差异。
注意原子电荷与氧化态无必然关系。氧化态是将电子转移人为极端化的产物,不能反映原子的真实带电情况。
(2)结果案例展示
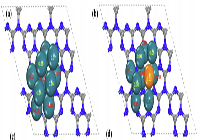
案例一: Bader charges of the (a) Pd10 and (b) Ag1Pd9 clusters on the 2D CNNs
说明:Based on the Bader charge analysis, Total electron transfer from the Pd10 and AgPd9 to 2D CNNs substrate were calculated to be 0.80|e| and 0.82 |e|, respectively. Introduction of Ag to the Pd10 cluster could effectively promote electron transference to 2D CNNs substrate.
来源文献:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125229
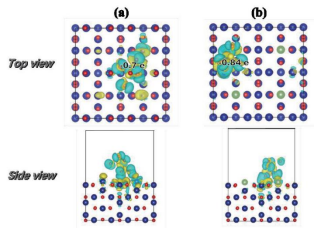
案例二:charge distribution before and after adsorption
说明:. The result of the simulation with the the {1 0 0} plane of the Pt nanoparticles showed that the positive charges of Cs and B increased after adsorption on the surface of the Pt (1 0 0). The Pt on the surface of Pt (1 0 0) only possessed a small amount of negative charge before capping with Cs2[closo-B12H12]. After capping with Cs2[closo-B12H12], the negative charge of the {1 0 0} plane of the Pt nanoparticle surface increased sharply. The B atoms on the surface of the {1 0 0} plane of the Pt nanoparticles possessed a significantly increased positive charge. This indicated that the Cs and B transferred their charge to the surface of the {1 0 0} plane of the Pt nanoparticles and their own charge was lost.
文献来源:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.01.047
第一性原理计算的基本思想是将多个原子构成的体系看成是由多个电子和原子核组成的系统,并根据量子力学的基本原理对问题进行最大限度的“非经验性”处理。它只需要5个基本常数(m0,e,h,c,kB)就可以计算出体系的能量和电子结构等物理性质。它可以确定已知材料的结构和基础性质,并实现原子级别的精准控制,是现阶段解决实验理论问题和预测新材料结构性能的有力工具。并且,第一性原理计算不需要开展真实的实验,极大地节省了实验成本,现已被广泛应用于化学、物理、生命科学和材料学等领域。
适合的研究方向包括但不限于:催化、电池、半导体、金属材料、非金属材料、合金、纳米材料等
可以计算的体系包括但不限于:晶体、非晶、二维材料、表面、界面、固体等
常用软件:VASP,MS,CP2K,QE等
可以计算的内容包括但不限于:
材料的几何结构参数(如键长、键角、二面角、晶格常数、原子位置等)
材料的电子结构信息(如电荷密度、电荷差分密度、态密度、能带、费米能级、功函数、ELF等)
材料的光学性质(如介电常数等)
材料的力学性质(如弹性模量等)
材料的磁学性质(如磁导率等)
材料的晶格动力学性质(如声子谱等)
材料的表面性质(如吸附能,催化计算等)
复合材料的性质(异质结等内容)等等