(1)定义及意义
能垒反映了基元步骤的快慢。第一性原理计算中最常见的能垒类型莫过于迁移能垒。它针对的是体相或表面中原子的迁移过程,例如在锂电池等领域的研究中,往往希望寻找相关原子迁移能垒较低的电极材料。
(2)结果案例示例
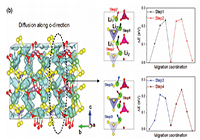
案例一:Schematic diagram and energy profile for cooperative migration along c-direction.
说明:Last, for the complex cooperative migration, it is very important to set the local energy minima structure and the migration pathway. To this end, we refer to the snapshot of the lithium trajectory in AIMD simulation. After relaxing the coordination of LiSxOy polyhedrons referred from AIMD simulation, we obtain the energy profile of Li-ion migration along c-direction and ab-plane via the cNEB calculations, as shown in Figure 7b; Figure S3, Supporting Information. The average migration barriers for the process along b-direction and ab-plane are 0.22 and 0.21 eV, respectively, which is slightly higher than that from AIMD simulation.
来源文献:DOI: 10.1002/smll.201906374
案例二:Calculated energy profiles and barriers
说明:Figures 2a-c depict the DFT-calculated energy profiles for Li + and Mg 2+ ion transport, while Figures 2d-f show images of the corresponding trajectories (for further details, see Figures S3-S5 in the Supporting Information). At the very early stages of discharge, when all inner-ring sites are empty, we found that the inner-ring sites are the only minima available for insertion. This indicates that there are no local minima at outer-ring sites, meaning that any foreign atom will fall spontaneously into the empty inner-ring. Once an ion occupies an inner-ring site, it requires considerable energy to escape (0.43 eV for Li + , and 0.51 eV for Mg 2+ ) due to relatively deep potential minima at the inner-ring sites, as shown in Figure 2a. This explains the trapping problem (i.e., the cyclical motion of a cation within the same inner-ring) often encountered experimentally upon the last stage of charging processes at RT, especially for the Mg x Mo 6 S 8 system. 34 Path 2 in Figure 2d is the trajectory adopted by an inserted cation as it overcomes these large energy barriers, and involves movement to another inner-ring site.
来源文献:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b03232
第一性原理计算的基本思想是将多个原子构成的体系看成是由多个电子和原子核组成的系统,并根据量子力学的基本原理对问题进行最大限度的“非经验性”处理。它只需要5个基本常数(m0,e,h,c,kB)就可以计算出体系的能量和电子结构等物理性质。它可以确定已知材料的结构和基础性质,并实现原子级别的精准控制,是现阶段解决实验理论问题和预测新材料结构性能的有力工具。并且,第一性原理计算不需要开展真实的实验,极大地节省了实验成本,现已被广泛应用于化学、物理、生命科学和材料学等领域。
适合的研究方向包括但不限于:催化、电池、半导体、金属材料、非金属材料、合金、纳米材料等
可以计算的体系包括但不限于:晶体、非晶、二维材料、表面、界面、固体等
常用软件:VASP,MS,CP2K,QE等
可以计算的内容包括但不限于:
材料的几何结构参数(如键长、键角、二面角、晶格常数、原子位置等)
材料的电子结构信息(如电荷密度、电荷差分密度、态密度、能带、费米能级、功函数、ELF等)
材料的光学性质(如介电常数等)
材料的力学性质(如弹性模量等)
材料的磁学性质(如磁导率等)
材料的晶格动力学性质(如声子谱等)
材料的表面性质(如吸附能,催化计算等)
复合材料的性质(异质结等内容)等等