(1)定义:互相粘着的两相界面,粘着前后单位表面积界面自由能的变化。粘附现象一般指两个互不相溶的相之间的粘着行为。两个互不溶解的液体之间、液体与固体以及气体与固体之间都可以发生粘附现象。液相与固相之间的粘附称为润湿,所以液固两相的粘附功也称润湿功。
(2)作用:说明组成界面的两相之间的粘附强弱。
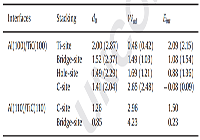
Table 2 Work of adhesion Wad (J/m2), interface energy Eint (J/m2) and interfacial separation d0 (Å) of Al/TiC interface. The values obtained without relaxation are also given in parentheses for comparison.
说明:In Table 2, the equilibrium spacing of interface d0, work of adhesion Wad and interface energy Eint are listed for Al(100)/TiC(100) and Al (110)/TiC(110) interfaces. It is very remarkable that work of adhesion of Al(100)/TiC(100) is obviously weak with respect to Al(110)/TiC(110). This is easy to understand. The surface energy of TiC(110) (3.55 J/m2) is larger than that of TiC(100) (1.74 J/m2). But, Al(100) and Al(110) have nearly the same surface energy (0.94 J/m2 and 0.99 J/m2). The larger surface energy leads to a stronger interface adhesion. Intermediate to the two extremes is the Hole-site and Bridge-site interfaces with the values of 1.69 J/m2 and 1.49 J/m2, respectively. These works of adhesion are in good agreement with the previous theoretical results: 0.51 J/m2 for Ti site, 1.44 J/m2 for Bridge-site and 2.63 J/m2 for C-site, and 0.51 J/m2 for Ti-site, 1.63 J/m2 for Bridge-site and 2.56 J/m2 for C-site. For Al(110)/TiC(110) system, Bridge-site (4.23 J/m2) is more stronger interface structure than C-site (2.96 J/m2).
文献来源:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.04.045
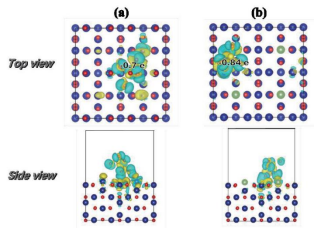
第一性原理计算的基本思想是将多个原子构成的体系看成是由多个电子和原子核组成的系统,并根据量子力学的基本原理对问题进行最大限度的“非经验性”处理。它只需要5个基本常数(m0,e,h,c,kB)就可以计算出体系的能量和电子结构等物理性质。它可以确定已知材料的结构和基础性质,并实现原子级别的精准控制,是现阶段解决实验理论问题和预测新材料结构性能的有力工具。并且,第一性原理计算不需要开展真实的实验,极大地节省了实验成本,现已被广泛应用于化学、物理、生命科学和材料学等领域。
适合的研究方向包括但不限于:催化、电池、半导体、金属材料、非金属材料、合金、纳米材料等
可以计算的体系包括但不限于:晶体、非晶、二维材料、表面、界面、固体等
常用软件:VASP,MS,CP2K,QE等
可以计算的内容包括但不限于:
材料的几何结构参数(如键长、键角、二面角、晶格常数、原子位置等)
材料的电子结构信息(如电荷密度、电荷差分密度、态密度、能带、费米能级、功函数、ELF等)
材料的光学性质(如介电常数等)
材料的力学性质(如弹性模量等)
材料的磁学性质(如磁导率等)
材料的晶格动力学性质(如声子谱等)
材料的表面性质(如吸附能,催化计算等)
复合材料的性质(异质结等内容)等等