(1)定义:晶格振动散射(声子散射)声子是一中非真实的准粒子,用来描述晶体原子热运动--晶格振动规律的一种能量量子。当晶体中的载流子运动时,会与热振动的晶格原子之间相互作用,吸收或发射声子;
(2)作用:材料中的载流子迁移率以及其他诸多物理性质通常与声子散射息息相关;
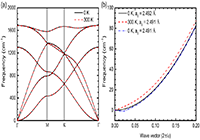
(a) Phonon dispersion of graphene along the high-symmetry lines, Γ-M-K-Γ. (b) Phonon dispersion curve of graphene for the ZA modes around the Γ point in the direction from Γ to M.
(3)说明:Figure 1 shows the phonon dispersion of graphene along the high-symmetry lines, Γ-M-K-Γ, calculated using the harmonic force constants at 0 and 300 K. Overall, the two sets of force constants lead to similar phonon dispersion curves, but two noticeable differences could be identified from Fig. 1(a). First, the finite temperature leads to a downshift of the phonon spectrum. For example, the obtained maximum frequency at the Γ point is reduced from 1690 to 1685 cm−1 if one uses the IFCs at 300 K to replace those at 0 K. Second, as shown in Fig. 1(b), the flexural out-of-plane acoustic (ZA) phonon branch follows ωZA ∝ q2 near the center of the Brillouin zone (the Γ point) if using the force constants at 0 K, but the ZA branch computed by the force constants at 300 K becomes linearized.
文献来源:DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.100.064306
第一性原理计算的基本思想是将多个原子构成的体系看成是由多个电子和原子核组成的系统,并根据量子力学的基本原理对问题进行最大限度的“非经验性”处理。它只需要5个基本常数(m0,e,h,c,kB)就可以计算出体系的能量和电子结构等物理性质。它可以确定已知材料的结构和基础性质,并实现原子级别的精准控制,是现阶段解决实验理论问题和预测新材料结构性能的有力工具。并且,第一性原理计算不需要开展真实的实验,极大地节省了实验成本,现已被广泛应用于化学、物理、生命科学和材料学等领域。
适合的研究方向包括但不限于:催化、电池、半导体、金属材料、非金属材料、合金、纳米材料等
可以计算的体系包括但不限于:晶体、非晶、二维材料、表面、界面、固体等
常用软件:VASP,MS,CP2K,QE等
可以计算的内容包括但不限于:
材料的几何结构参数(如键长、键角、二面角、晶格常数、原子位置等)
材料的电子结构信息(如电荷密度、电荷差分密度、态密度、能带、费米能级、功函数、ELF等)
材料的光学性质(如介电常数等)
材料的力学性质(如弹性模量等)
材料的磁学性质(如磁导率等)
材料的晶格动力学性质(如声子谱等)
材料的表面性质(如吸附能,催化计算等)
复合材料的性质(异质结等内容)等等