(1)定义:密度泛函理论(density functional theory,简称DFT)是指从电子密度出发,通过各种近似理论求解Kohn-Sham(KS)方程得到多电子体系能量及其它性质的方法。局域密度近似(LDA)或广义梯度近似(GGA)中没有忽略电子与其自身的相互作用,使得KS轨道离散于整个空间,表现为一定程度上的非局域化。而在传统量化Harteen-Fock(HF)方法中,电子的自相互作用抵消,从而可以正确描述电子间的交换项。
(2)作用:杂化泛函能够更好的描述电子自相互作用比较严重的体系,并且可以通过改变线性组合系数来调节HF交换泛函与DFT交换泛函的比例,使得计算结果更为精确,更加的接近实验的真实结果。HSE06是目前运用最广泛的杂化泛函方法,一般适用于半导体体系。
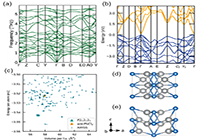
Figure 3. (a) The phonon band structure of the anti-PbCl2-like Ag2Se phase. The structure is dynamically stable, since all modes have positive frequencies across the first Brillouin zone. (b) The electronic band structure of the anti-PbCl2-like phase computed using the HSE06 hybrid functional, showing that it is a narrow-band-gap semiconductor. (c) The total energy plotted against the volume per formula unit for structures obtained through searching (AIRSS) as well as the orthorhombic P212121 (▲) and the anti-PbCl2-like P21/n (★) phases. The PBEsol exchange-correlation functional is used here. (d) The P2 unit cell reported by Günter and Keusch. (e) The unit cell in (d) optimized using DFT with the PBEsol functional. Significant structural changes take placethe adjacent [200] planes shear in the [001] direction, and the Ag atoms move to different sites.
(3)说明:The calculated electronic structure of the anti-PbCl2-like phase shows that it is a semiconductor with a narrow gap of ∼0.13 eV at the Γ-point, as shown in Figure 3b. We found that the orthorhombic polymorph also has a narrow gap, at ∼0.05 eV, consistent with previous DFT work.47 The band-gap openings only take place with the HSE06 function, as both polymorphs have no band gap if the PBEsol functional is used instead. These band gaps are quite close to experimentally determined optical band gap measurements for these two polymorphs of Ag2Se.
文献来源:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c02045
第一性原理计算的基本思想是将多个原子构成的体系看成是由多个电子和原子核组成的系统,并根据量子力学的基本原理对问题进行最大限度的“非经验性”处理。它只需要5个基本常数(m0,e,h,c,kB)就可以计算出体系的能量和电子结构等物理性质。它可以确定已知材料的结构和基础性质,并实现原子级别的精准控制,是现阶段解决实验理论问题和预测新材料结构性能的有力工具。并且,第一性原理计算不需要开展真实的实验,极大地节省了实验成本,现已被广泛应用于化学、物理、生命科学和材料学等领域。
适合的研究方向包括但不限于:催化、电池、半导体、金属材料、非金属材料、合金、纳米材料等
可以计算的体系包括但不限于:晶体、非晶、二维材料、表面、界面、固体等
常用软件:VASP,MS,CP2K,QE等
可以计算的内容包括但不限于:
材料的几何结构参数(如键长、键角、二面角、晶格常数、原子位置等)
材料的电子结构信息(如电荷密度、电荷差分密度、态密度、能带、费米能级、功函数、ELF等)
材料的光学性质(如介电常数等)
材料的力学性质(如弹性模量等)
材料的磁学性质(如磁导率等)
材料的晶格动力学性质(如声子谱等)
材料的表面性质(如吸附能,催化计算等)
复合材料的性质(异质结等内容)等等