离子键以外的非共价相互作用(noncovalent interaction)即为通常大家所说的弱相互作用。该研究常见于各种方向的文章中。
常规的计算是计算结合能等数据,见“2能量相关计算”部分。
近年来,随着Multiwfn软件越来越成熟,其支持的一些弱相互作用分析方法也被广泛使用。目前常用的分析方法有RDG IGM等
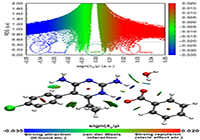
Revealing Noncovalent Interactions (RDG)
The top of Fig. 7 presents the plot of RGD versus the sign(λ2)ρ plot for I and bottom shows the various types of interactions in the real space of the molecule. The majority of interactions between different constituents of I mainly consists of vdW types of interactions as revealed by the dominant green color in the bottom figure and spikes located around zero on top figure. The only stronger attractive interaction i.e. the hydrogen bonding is present between the pyrimethamine and the carboxylic group of benzoic acid. The interactions between water and both of the other components are much weaker than the aforementioned interactions. This indicates that though water is important for unit cell packing but the significant role for dimer formation is only played by the hydrogen bonding interaction between the major components of I.
文献来源:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128183
Independent Gradient Model (IGM)
Non-covalent interactions between O-NH2 and GSH using the IGM method; δginter = 0.01 a.u. isosurfaces coloured according to the BGR scheme over the signed electron density range -0.05 < sign (λ2) ρ < 0.05 a.u.
As shown in Figure 3, the extent of interaction could be indicated by the volume of the interacting regions between O-NH2 and GSH. Green indicates weak interactions (such as van der Waals-type interactions) while blue denotes stronger and more stable interactions (such as hydrogen bonds). The analysis clearly shows that amide unit of O-NH 2 could generate the stabilized intermolecular hydrogen bonds (such as N−H···O) with the carboxyl unit (on the glycine moiety of GSH). Besides, possible hydrogen bonds could be formed between the carboxyl moiety of O-NH 2 (such as C−H···O and N−H···O) and the glutamic acid moiety of GSH in the structure of an intermediate binding. Consequently, two reactive sites (arylthioether moiety and SH moiety) would be dragged within a shorter distance by these intermolecular interactions, which contributed to the selectivity of O-NH 2 to GSH. When the methyl moiety replaced in the 4-position of thiophenol, the stabilized intermolecular hydrogen bonds could be difficult to be formed, which could lead to a longer distance and flexibility between the two reactive sites and further decrease the possibility of reaction with GSH. Therefore, probe O-CH 3 could not detect GSH and Cys/Hcy selectively.
文献来源:https://doi.org/10.1039/C9AN00115H
量子化学(quantum chemistry)是理论化学的一个分支学科,是应用量子力学的基本原理和方法研究化学问题的一门基础科学。研究范围包括稳定和不稳定分子的结构、性能及其结构与性能之间的关系;分子与分子之间的相互作用;分子与分子之间的相互碰撞和相互反应等问题。
适合的研究方向包括但不限于:有机合成、方法学研究、高分子等
可以计算的体系包括但不限于:小分子、团簇、低聚物、自由基、离子等
常用软件:Gaussian,ORCA,dmol3等
可以计算的内容包括但不限于:
分子性质,如键长键角二面角、HOMO/LUMO、电荷分布、键级、偶极矩、极化率、芳香性、静电势、Fukui函数、激发态研究等
光谱预测,如红外、紫外、拉曼、荧光、磷光、核磁、圆二色谱、旋光度等
能量计算,如结合能、解离能、电离能、弱相互作用分析等
反应相关,如过渡态搜索、势能面扫描、反应位点预测、反应路径、反应机理研究等