芳香性分子在能量、键长、稳定性、反应性、磁诱导电流、电子离域性等方面都有独特的性质。芳香性的判别通常遵循Huckel的4n+2规则。近年来ICSS分析和NICS分析显示出了更大的前景。
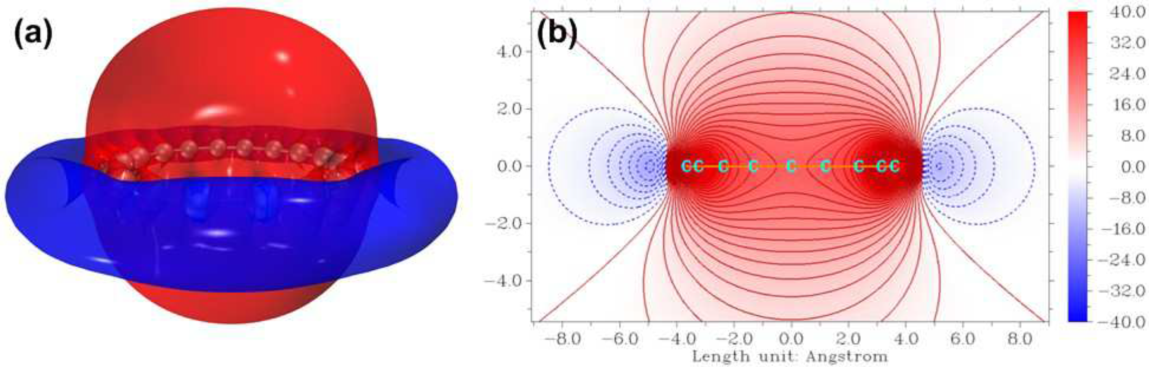
ICSS of the cyclo[18]carbon: (a) isosurface of ICSSZZ (isovalue = 8.0 ppm) and (b) color-filled contour map of ICSSZZ in the slice plane perpendicular to the ring. The color scale is given in ppm.
The iso-chemical shielding surface (ICSS) is a real space function closely related to the well-known nucleus-independent chemical shifts (NICS), which can be used to evaluate the aromaticity of cyclic molecules or local rings. The NICS studies chemical shielding at specific points against external magnetic field, while the ICSS extends its idea to the entire three-dimension space. The ICSS method calculates magnetic shielding tensor at every evenly distributed grid point around the system and plots specific component of the tensors as a isosurface map, which can unambiguously reveal the extent of magnetic shielding and deshielding effects in different regions originating from delocalized electrons. The isosurface of ZZ component of the ICSS (ICSSZZ) of the cyclo[18]carbon is presented in Fig. 7(a). It can be seen that there are significant shielding regions protrudes in the direction perpendicular to the ring plane of the cyclo[18]carbon and a closed deshielding circular isosurface surrounded it. The feature of ICSSZZ distribution of the cyclo[18]carbon further consolidates the conclusion that the cyclo[18]carbon should be considered to be a system with significant aromaticity. The ICSSZZ can be examined in more depth by inspecting the slice plane perpendicular to the cyclo[18]carbon ring, as shown in Fig. 7(b). From this map one can see that the magnetic shielding effect of the cyclo[18]carbon is fairly large and the change in the inner region of the ring is very smooth. The ICSSZZ values calculated at the center of the ring and at 1 Å above this point, namely, ICSSZZ(0) and ICSSZZ(1), are 25.7 and 23.7 ppm, respectively, while the corresponding values of benzene are found to be 16.1 and 29.9 ppm. The difference in ICSSZZ(1) values for the two systems implies that the out-of-plane p aromaticity of benzene is larger than that of the cyclo[18]carbon, while the much larger ICSSZZ(0) of the cyclo[18]carbon should source from its unique in-plane p aromaticity, which is missing in benzene.
文献来源:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.04.099
量子化学(quantum chemistry)是理论化学的一个分支学科,是应用量子力学的基本原理和方法研究化学问题的一门基础科学。研究范围包括稳定和不稳定分子的结构、性能及其结构与性能之间的关系;分子与分子之间的相互作用;分子与分子之间的相互碰撞和相互反应等问题。
适合的研究方向包括但不限于:有机合成、方法学研究、高分子等
可以计算的体系包括但不限于:小分子、团簇、低聚物、自由基、离子等
常用软件:Gaussian,ORCA,dmol3等
可以计算的内容包括但不限于:
分子性质,如键长键角二面角、HOMO/LUMO、电荷分布、键级、偶极矩、极化率、芳香性、静电势、Fukui函数、激发态研究等
光谱预测,如红外、紫外、拉曼、荧光、磷光、核磁、圆二色谱、旋光度等
能量计算,如结合能、解离能、电离能、弱相互作用分析等
反应相关,如过渡态搜索、势能面扫描、反应位点预测、反应路径、反应机理研究等